https://www.yna.co.kr/view/AKR20220713003700075?section=international/all&site=topnews01
우주진화·외계생명체 비밀 풀리나…웹망원경, 외계행성 물 확인(종합) | 연합뉴스
(로스앤젤레스=연합뉴스) 정윤섭 특파원 = 춤추며 충돌하는 은하, 별들의 요람에서 탄생한 아기별과 생을 다한 별이 뿜어내는 가스까지 제임스 웹 ...
www.yna.co.kr
우주진화·외계생명체 비밀 풀리나…웹망원경, 외계행성 물 확인(종합)
송고시간2022-07-13 03:13 정윤섭 기자
NASA, 최강 웹망원경이 찍은 우주 깊은 곳 풀컬러 사진·자료 공개
죽어가는 별이 내뿜는 가스·먼지 포착…은하간 상호충돌 모습도 담아
1천150광년 떨어진 외계행성의 대기에서 구름·연무·물의 특징 파악
미항공우주국 NASA가 이런 짓을 저질렀다 해서 난리라, 느닷없이 그 홈페이지로 들어가 이번에 저네가 작년인가에 우주로 쏘아 올렸다는 제임스 웹 우주망원경 the James Webb Space Telescope이 촬영해 처음으로 공개한 사진들이라는 양상을 훑어봤다.
보니 고화질로 우주 사진들이라며 공개해 놨더라. 공개했으니 맘대로 사용하라는 뜻이다. 그래서 나도 그 의도 살려 맘대로 다운로드해 맘대로 사용하고자 한다. 미국 만세!! 나사 만세!!!
그건 그렇고 아무리 최신 망원경이라 해서 저리 나올 수는 없다. 다 포샵 처리한 걸로 안다.

문제의 망원경이 이렇댄다. 뭐 낙하산 같구만?
이 친구가 촬영한 사진들은 아래에서 공개한다.
https://www.nasa.gov/webbfirstimages
First Images from the James Webb Space Telescope
The dawn of a new era in astronomy has begun as the world gets its first look at the full capabilities of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
www.nasa.gov
공개 목록은 이렇다.
SMACS 0723: Webb has delivered the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe so far – and in only 12.5 hours. For a person standing on Earth looking up, the field of view for this new image, a color composite of multiple exposures each about two hours long, is approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length. This deep field uses a lensing galaxy cluster to find some of the most distant galaxies ever detected. This image only scratches the surface of Webb’s capabilities in studying deep fields and tracing galaxies back to the beginning of cosmic time.
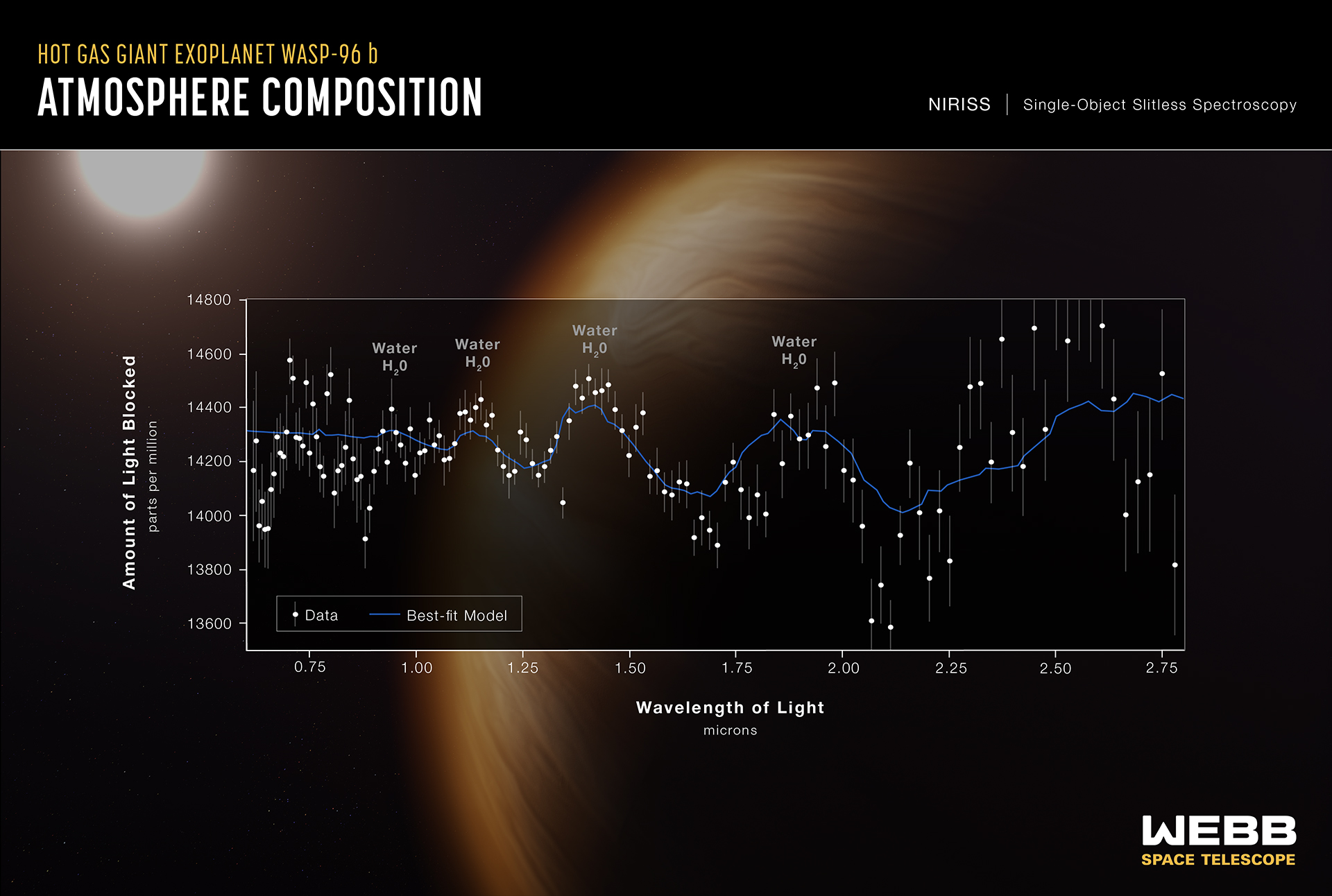
WASP-96b (spectrum): Webb’s detailed observation of this hot, puffy planet outside our solar system reveals the clear signature of water, along with evidence of haze and clouds that previous studies of this planet did not detect. With Webb’s first detection of water in the atmosphere of an exoplanet, it will now set out to study hundreds of other systems to understand what other planetary atmospheres are made of.
Southern Ring Nebula: This planetary nebula, an expanding cloud of gas that surrounds a dying star, is approximately 2,000 light years away. Here, Webb’s powerful infrared eyes bring a second dying star into full view for the first time. From birth to death as a planetary nebula, Webb can explore the expelling shells of dust and gas of aging stars that may one day become a new star or planet.
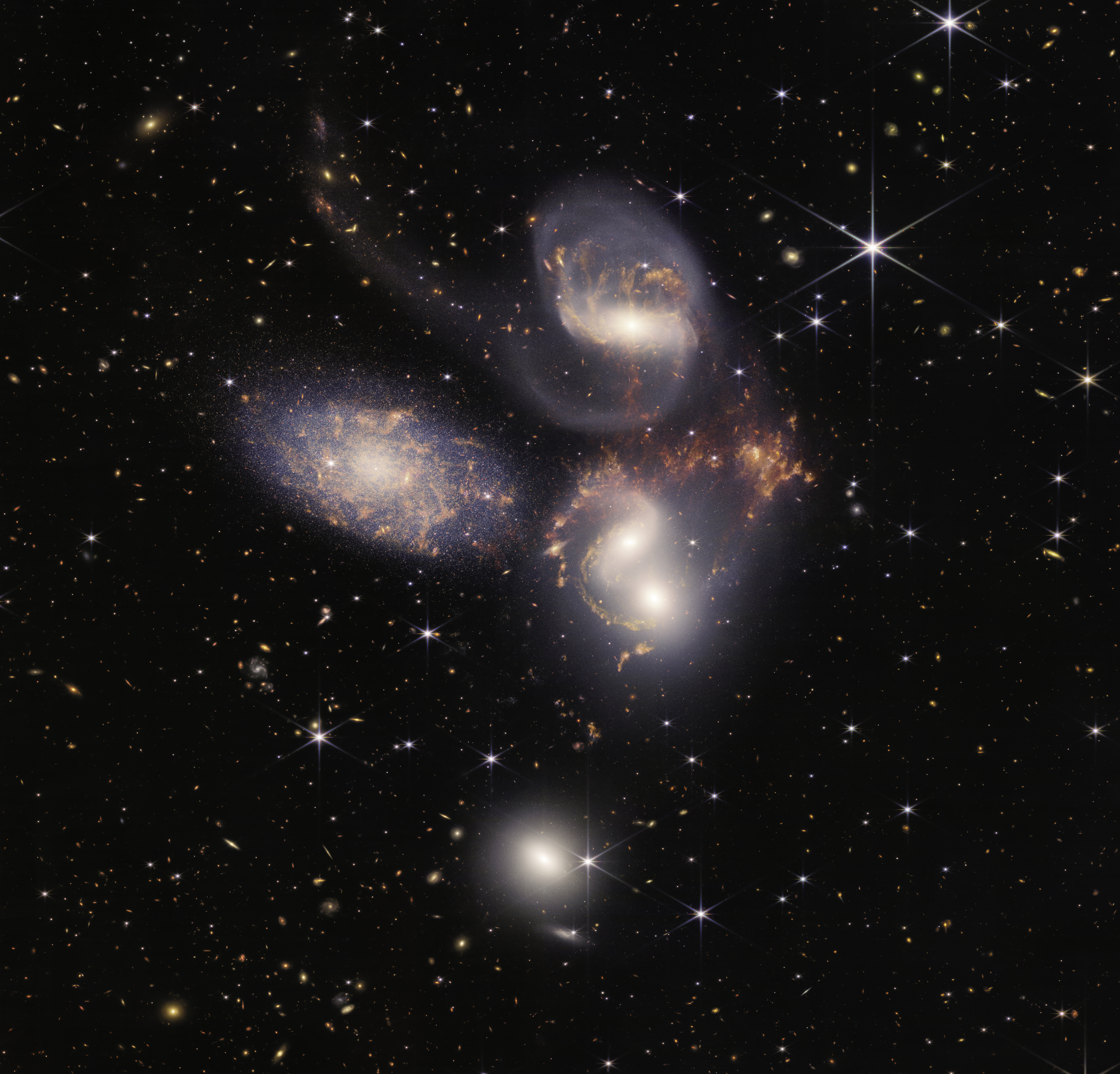
Stephan’s Quintet: Webb’s view of this compact group of galaxies, located in the constellation Pegasus, pierced through the shroud of dust surrounding the center of one galaxy, to reveal the velocity and composition of the gas near its supermassive black hole. Now, scientists can get a rare look, in unprecedented detail, at how interacting galaxies are triggering star formation in each other and how the gas in these galaxies is being disturbed.
Carina Nebula: Webb’s look at the ‘Cosmic Cliffs’ in the Carina Nebula unveils the earliest, rapid phases of star formation that were previously hidden. Looking at this star-forming region in the southern constellation Carina, as well as others like it, Webb can see newly forming stars and study the gas and dust that made them.

이건 뭐 공상과학영화를 보는 듯한 착각을 유발하는데, 앞 사진 설명은 이렇다. 우주천문은 내가 문외한이니 그냥 인용만 한다.
Webb’s First Deep Field, this image of galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 is overflowing with detail.
Thousands of galaxies – including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared – have appeared in Webb’s view for the first time. This slice of the vast universe covers a patch of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length by someone on the ground.

이건 세포 사진 같은데 이렇댄다.
Stephan’s Quintet, a visual grouping of five galaxies, is best known for being prominently featured in the holiday classic film, “It’s a Wonderful Life.” Today, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope reveals Stephan’s Quintet in a new light. This enormous mosaic is Webb’s largest image to date, covering about one-fifth of the Moon’s diameter. It contains over 150 million pixels and is constructed from almost 1,000 separate image files. The information from Webb provides new insights into how galactic interactions may have driven galaxy evolution in the early universe.
With its powerful, infrared vision and extremely high spatial resolution, Webb shows never-before-seen details in this galaxy group. Sparkling clusters of millions of young stars and starburst regions of fresh star birth grace the image. Sweeping tails of gas, dust and stars are being pulled from several of the galaxies due to gravitational interactions. Most dramatically, Webb captures huge shock waves as one of the galaxies, NGC 7318B, smashes through the cluster.

이 사진이 언론에는 대문으로 많이 소개되던데, 이유는 볼짝 없다. 뭔가 있어 보이잖아? 앞 사진 설명은 이렇다.
This landscape of “mountains” and “valleys” speckled with glittering stars is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region called NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals for the first time previously invisible areas of star birth.
Called the Cosmic Cliffs, Webb’s seemingly three-dimensional picture looks like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening. In reality, it is the edge of the giant, gaseous cavity within NGC 3324, and the tallest “peaks” in this image are about 7 light-years high. The cavernous area has been carved from the nebula by the intense ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from extremely massive, hot, young stars located in the center of the bubble, above the area shown in this image.
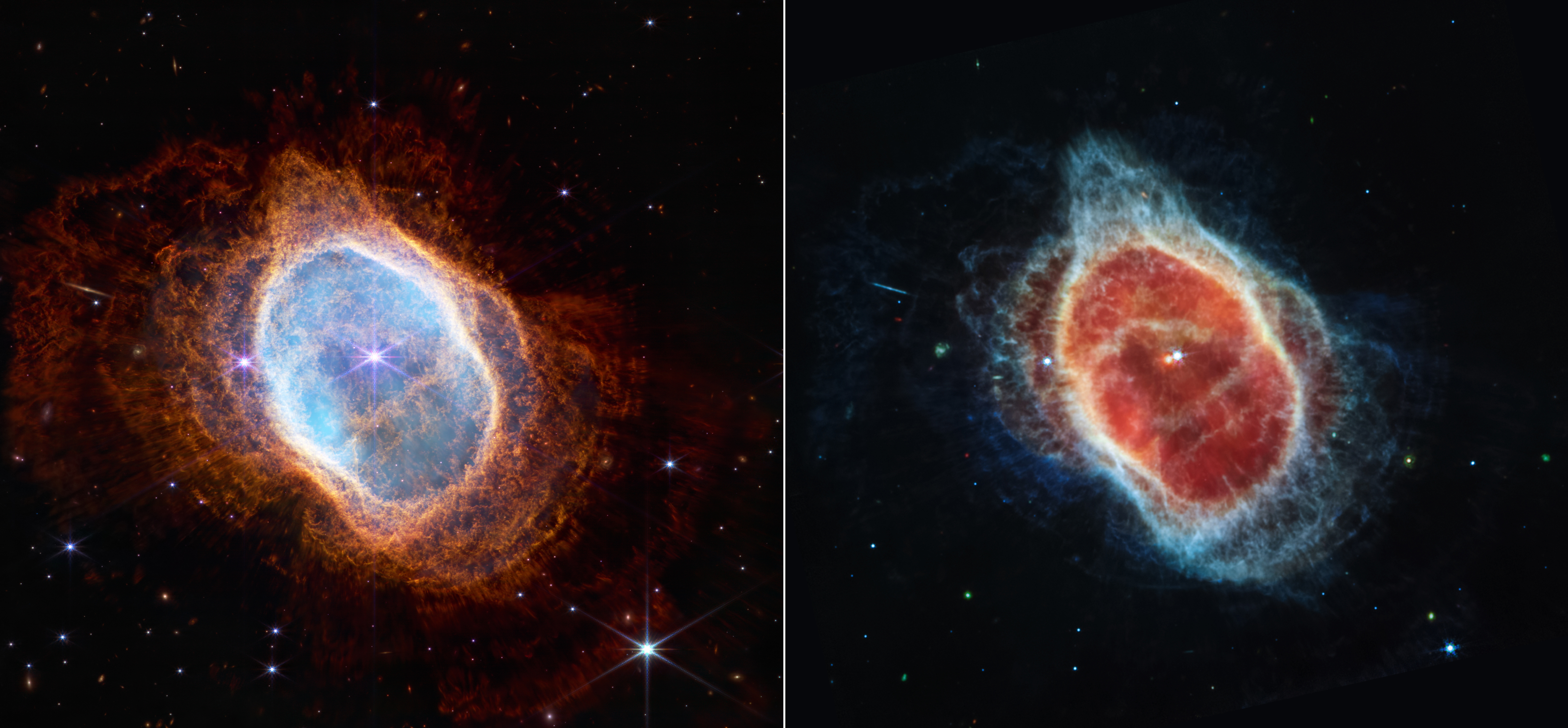

이건 뭐 아메바 같기도 한데, 이 설명은 이렇다.
Some stars save the best for last.
The dimmer star at the center of this scene has been sending out rings of gas and dust for thousands of years in all directions, and NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed for the first time that this star is cloaked in dust.
Two cameras aboard Webb captured the latest image of this planetary nebula, cataloged as NGC 3132, and known informally as the Southern Ring Nebula. It is approximately 2,500 light-years away.
Webb will allow astronomers to dig into many more specifics about planetary nebulae like this one – clouds of gas and dust expelled by dying stars. Understanding which molecules are present, and where they lie throughout the shells of gas and dust will help researchers refine their knowledge of these objects.

우주도 노안이 왔나? 뿌옇다. Stephan's Quintet (MIRI Image) 이랜다. 아래와 같은 설명 대목이 있다. 뭔 말인지 모르겠다.
In this image, red denotes dusty, star-forming regions, as well as extremely distant, early galaxies and galaxies enshrouded in thick dust. Blue point sources show stars or star clusters without dust. Diffuse areas of blue indicate dust that has a significant amount of large hydrocarbon molecules. For small background galaxies scattered throughout the image, the green and yellow colors represent more distant, earlier galaxies that are rich in these hydrocarbons as well.

앞 사진은 “Cosmic Cliffs” in the Carina Nebula (NIRCam and MIRI Composite Image) 이랜다.
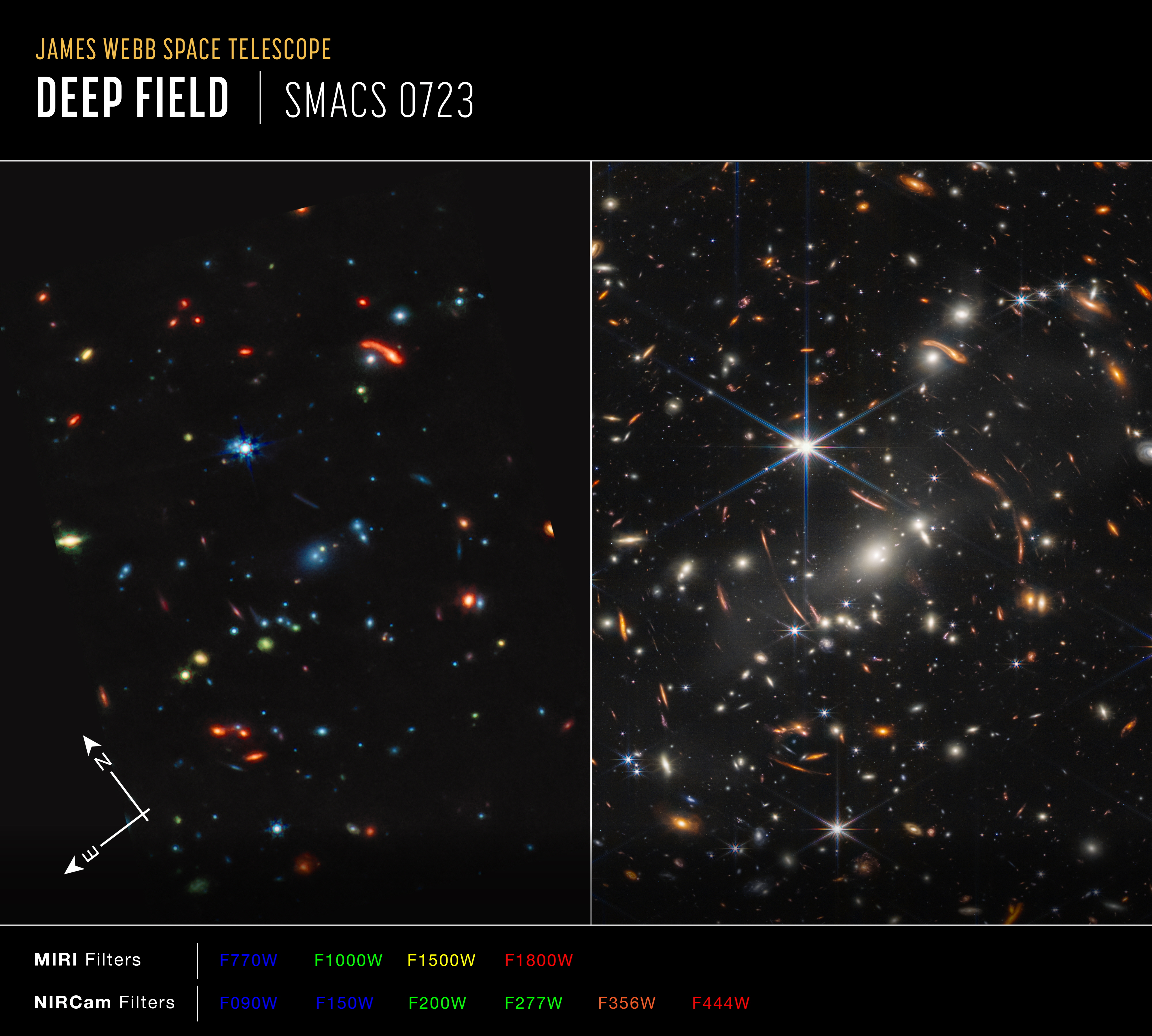
앞은 Webb's First Deep Field (MIRI and NIRCam Side-by-Side Compass Image) 라고
이건 뭔가 봐도 난 모르겠다.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the distinct signature of water, along with evidence for clouds and haze, in the atmosphere surrounding a hot, puffy gas giant planet orbiting a distant Sun-like star.
The observation, which reveals the presence of specific gas molecules based on tiny decreases in the brightness of precise colors of light, is the most detailed of its kind to date, demonstrating Webb’s unprecedented ability to analyze atmospheres hundreds of light-years away.
While the Hubble Space Telescope has analyzed numerous exoplanet atmospheres over the past two decades, capturing the first clear detection of water in 2013, Webb’s immediate and more detailed observation marks a giant leap forward in the quest to characterize potentially habitable planets beyond Earth.
'NEWS & THESIS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Relics excavated from 1,300 year old Astana Tombs on display in Seoul (0) | 2022.07.17 |
|---|---|
| 연합뉴스가 문화아카데미를 개설합니다 (1) | 2022.07.13 |
| 20년 만에 다시 헤집었다는 완주 원상운 고분 (1) | 2022.07.12 |
| 김포 장릉 주변 아파트 건설이 문화재 훼손인가를 법원이 판결한 요지 (1) | 2022.07.11 |
| 5세기 글자 새김 쇠칼? 없어! 배째!!! 일본판 훈민정음 해례본 은닉 사건 (0) | 2022.07.11 |




댓글